Overview
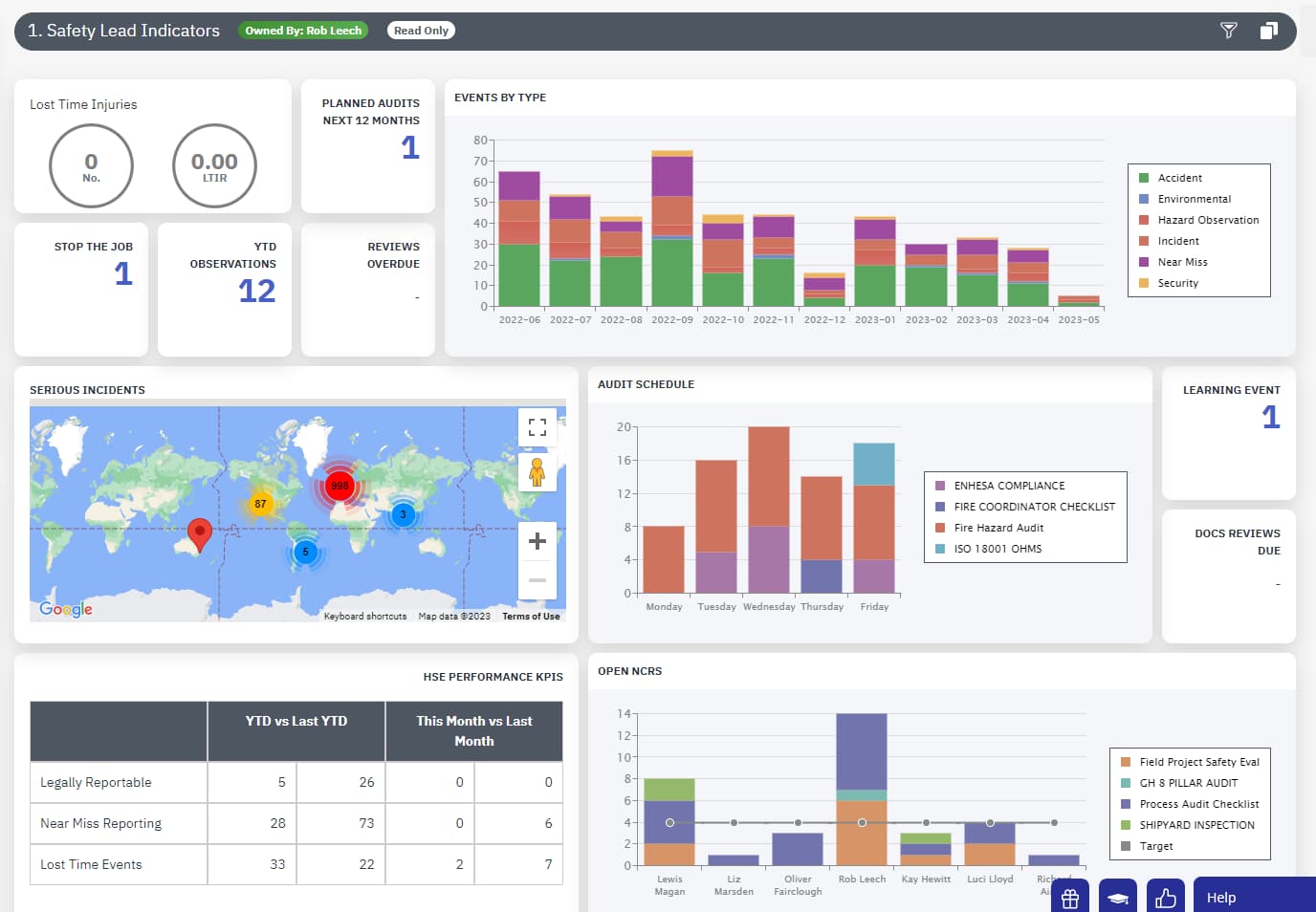
Focus your efforts on achieving zero with Health & Safety Software
Audit & Inspections
Fully automate your audit process. Manage all your data from one central location.
Lone Worker (StaySafe)
24/7 protection for your workers with our Lone Worker App, powered by StaySafe.
Control of Work
Gain faster insights with Incident Reporting Software
Incident Management
Gain faster insights with Incident Reporting Software
Risk Management
Our risk assessment software helps you to standardise your approach to risk management.
Emergency Response & Critical Event
Better equip your business with our smart & reliable system
Safety Management Software - Powered by eCompliance
Eliminate common safety barriers and empower your workforce with safety management software powered by eCompliance.