Corrosive Meaning & Definition
What Does Corrosive Mean?
The term “corrosive” simply refers to a property of materials which can destroy other materials they come into contact with. Most corrosives are either bases, oxidizers, or acids, and are commonly found in different work environments.
Corrosive substances are capable of destroying other substances as they cause a chemical reaction. Any chemical that can dissolve the core structure of another is defined as a corrosive.
For instance, hydrochloric acid is a common example. When spilled on human skin, it immediately starts corroding body tissue. Corrosion can also take years to occur, such as rust on iron. Common examples of corrosives include:
- Sulfuric acid
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Hydrochloric acid
- Bromine
The Importance of Properly Handling Corrosive Substances
Corrosive substances can cause serious damage, both to humans and to property or assets in the workplace. Certain corrosives can immediately start eating away at body tissue, and result in serious injury.
Recovery is often long and painful, which is why it’s so important for companies to ensure worker safety when handling corrosive liquids and solids. Apart from the fact that corrosives can cause serious harm to body tissue, there are other hazards to worry about as well.
For instance, some corrosive liquids can cause a violet chemical reaction, resulting in explosions, exothermic reactions or may even result in a fire. It’s important for workers to know that certain acids might react violently with other metals, releasing hydrogen, which is a highly flammable gas.
Furthermore, certain acids are robust oxidizing agents and if exposed to organic or other oxidizable materials, may cause a violent reaction. If workers aren’t aware of these hazards, there’s an elevated risk of an hazardous event or injury.

Common Risks When Using Corrosive Substances
Corrosive substances pose serious harm to workers in various ways, as discussed below.
Inhaling
Inhaling corrosive vapours can cause irritation in the lungs, throat, and a person’s nose. This can result in serious respiratory issues and excessive coughing. However, certain gases, such as hydrofluoric acid can leave severe burns on a person’s throats, windpipe, or their nasal airways.
When dealing with corrosive gases, it’s imperative to ensure that the workplace is properly ventilated. Certain workplaces use high-end ventilation systems to ensure that harmful gases are removed from the work site.
Furthermore, in some cases, a gas monitoring system with alarms might also be required. To prevent inhalation, workers may also be requested to wear respirators or face masks.
Ingestion
Ingesting a corrosive substance can prove to be incredibly harmful, and can result in body tissue damage. The lining in a person’s mouth, throat, the airways, and the stomach, requiring immediate medical attention.
If ingested, corrosive liquids in the workplace can result in serious harm. It’s important for companies to think about offering full-faced PPE to workers. This can prevent accidental ingestion.
When workers have to deal with corrosive liquids, it’s important for employers to make sure that they break down tasks and review sequences to minimize any risks.
Absorption
Absorbing corrosive chemicals can result in serious harm to a person’s internal organs. For instance, hydrofluoric acid doesn’t damage the body immediately. In fact, exposure accumulates over time in the long run.
It weakens the victim’s bones, causing the bone structure to generate over time and damaging the heart, the intestines, and the nerves. Another example is pesticides. Several pesticides don’t cause harm immediately. Instead, they build up in the body over time, and cause damage to a person’s nervous system.
Unfiltered Contact
If there is direct contact with any chemical, it’s likely to result in instant tissue damage. Irritation on the skin is a likely effect, which would then result in burns or blisters. In case of direct contact with the eyes, there’s a risk of blindness or scarring.
Direct contact can result in a serious medical issue, which is why it’s important for employers to provide adequate PPE to employees. Offering training to workers on how to move corrosive liquids from one container to another is also important, as that’s when most accidents generally occur.
Establishing Safe Work Practices and Prioritizing First Aid
It’s important for companies to train workers to follow safe work practices. They need to make sure that they check the labels and the Safety Data Sheets so that they know exactly what materials they’re working with.
More importantly, companies need to ensure that the area is properly ventilated to reduce any airborne exposure, and it’s also important to properly label containers to reduce exposures or spills.
When dealing with corrosive substances, companies must also ensure that they offer first aid. Employees must have proper training on how to respond in case of an accident.
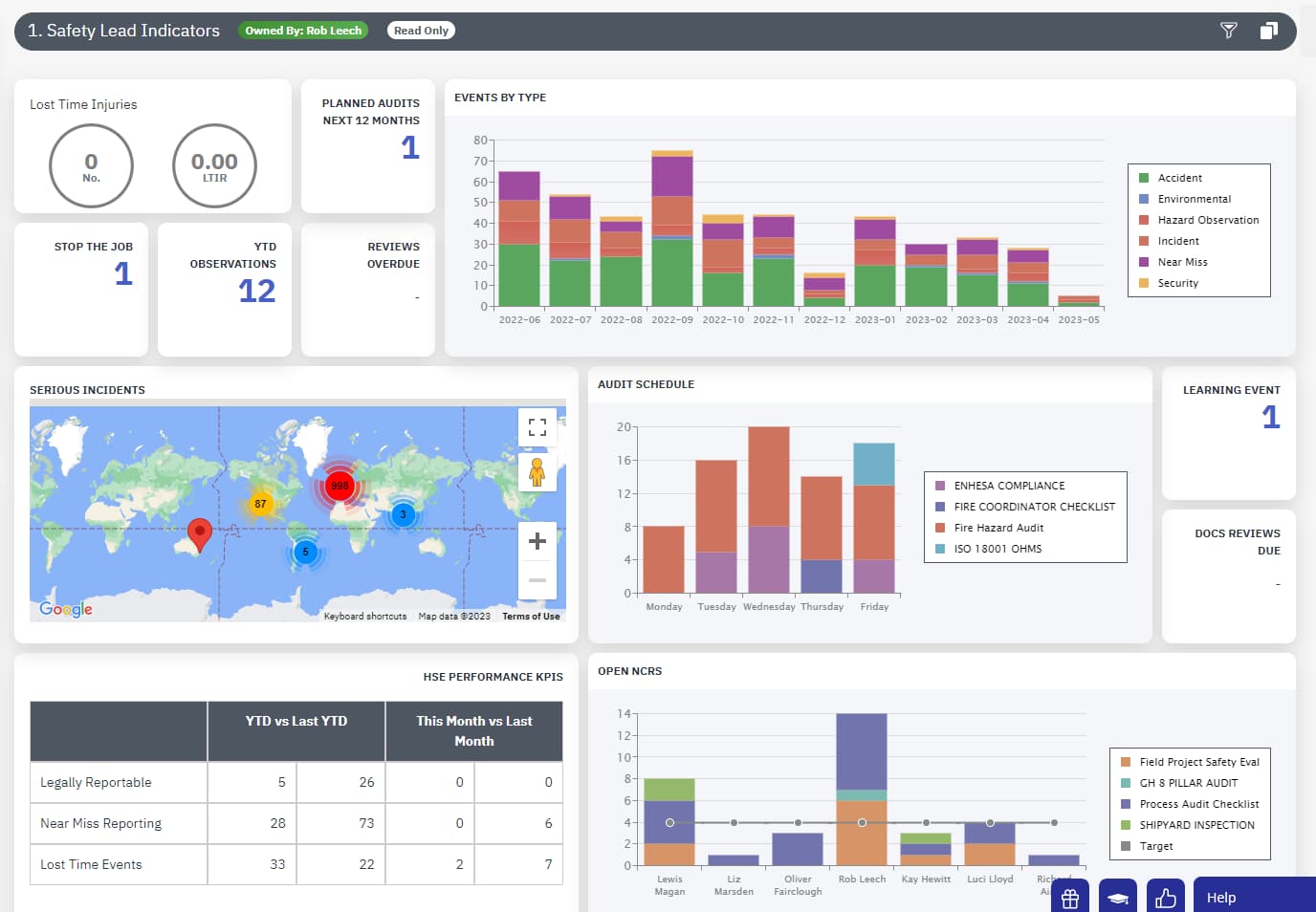
Use EcoOnline’s Chemical Software to Improve Worker Safety
EcoOnline’s Chemical Safety Software allows companies to easily record the use of all corrosive substances in the workplace. The platform also lets employers to provide important information about different corrosive substances and how to handle them safely.