Hazard Meaning & Definition
What is a Hazard?
A hazard is defined as anything that can be a potential source of harm, or something that could have an adverse health effect on those who come into contact with it.
A hazard can be a substance, an object, a series of events, or even circumstances, that may result in potential injury, either mental or physical. Hazards can also lead to property damage, or result in a loss of value of something.
There are different kinds of hazards, including technological, natural, or anthropogenic hazards. In the workplace, it’s important for companies to take note of different hazards and determine how to deal with them.
Hazard vs. Risk
While the word “hazard” is often used interchangeably with “risk,” the two actually have different meanings. Hazards, as mentioned above, are a source of harm.
Risk, on the other hand, defines the probability of a person getting harmed if they are exposed to hazards. Understanding the difference between the two is essential, since they both play such an important role in helping companies improve safety in the workplace.
Types of Hazards
Hazards can be categorized into different categories, as discussed below.
Safety Hazards
Probably the most common types of hazards in the workplace are safety hazards. These can affect anyone who works on a particular site, such as employees. Common examples of safety hazards include falls, electrical hazards, or hazards related to the use of dangerous machinery.
Environmental Hazards
Environmental hazards are those that can result in the degradation or deterioration of the environment, including damage to the soil, vegetation, or the water in the surroundings.
Water contamination is a common example of an environmental hazard. Companies must carefully determine all environmental hazards and take steps to mitigate or eliminate them.
Chemical Hazards
Common in organizations that work with harmful substances, chemical hazards can affect employees who generally work with flammable gases or harmful liquids.
Exposure to chemical hazards can result in injuries, irritation, respiratory issues, and can even cause death.
Ergonomic Hazards
Ergonomic hazards can affect employees who regularly strain their bodies. For instance, construction workers who regularly lift heavy loads are exposed to greater ergonomic risk. Another common ergonomic risk is sitting in a sedentary position for too long.
Companies must ensure that workers have proper training and the tools that they require to mitigate the risk posed by such hazards.
Physical Hazards
Physical hazards include exposure to UV rays, working for too long in the sun, or radiation, often as a result of working in a harsh environment.
It’s important to factor these in and prepare a plan for mitigating the risks that they pose.
Work-Related Hazards
These hazards are generally caused due to an isolated work environment, excessive workload, strain, and stress. Anybody can experience these hazards. A common example is burnout.
How to Mitigate the Risk Posed by Different Hazards
Most companies rely on a risk assessment procedure to identify and mitigate the risks posed by different hazards. Here’s how it works.
1. Identify and Categorize Hazards
The first step is to identify all the different hazards in the workplace. Safety personnel often conduct interviews and surveys, or inspect the workplace to make a list of all hazards.
Once they have the list of hazards, they start to categorize them. Categorizing hazards is important, as the ones that pose the highest risk must be dealt with first.
2. Prepare a Plan for Mitigation
Once the safety personnel have an idea about the risks posed by different hazards, they start working on a plan to mitigate or eliminate them.
It’s understandable that not all risks can be fully eliminated. In that case, companies usually look for ways to mitigate these risks as much as possible.
3. Communicate with Employees
Once the company has a plan in place, the next step is to communicate with your managers, supervisors, and other employees. Every employee should know about different hazards in the workplace, and what they must do to mitigate them.
4. Monitor Safety Performance Regularly
Due to the dynamic nature of modern work environments, new hazards may arise from time to time. That’s why it’s important for companies to monitor safety performance regularly.
They must also create a system for reporting near misses or other safety events that may help the company identify different hazards.
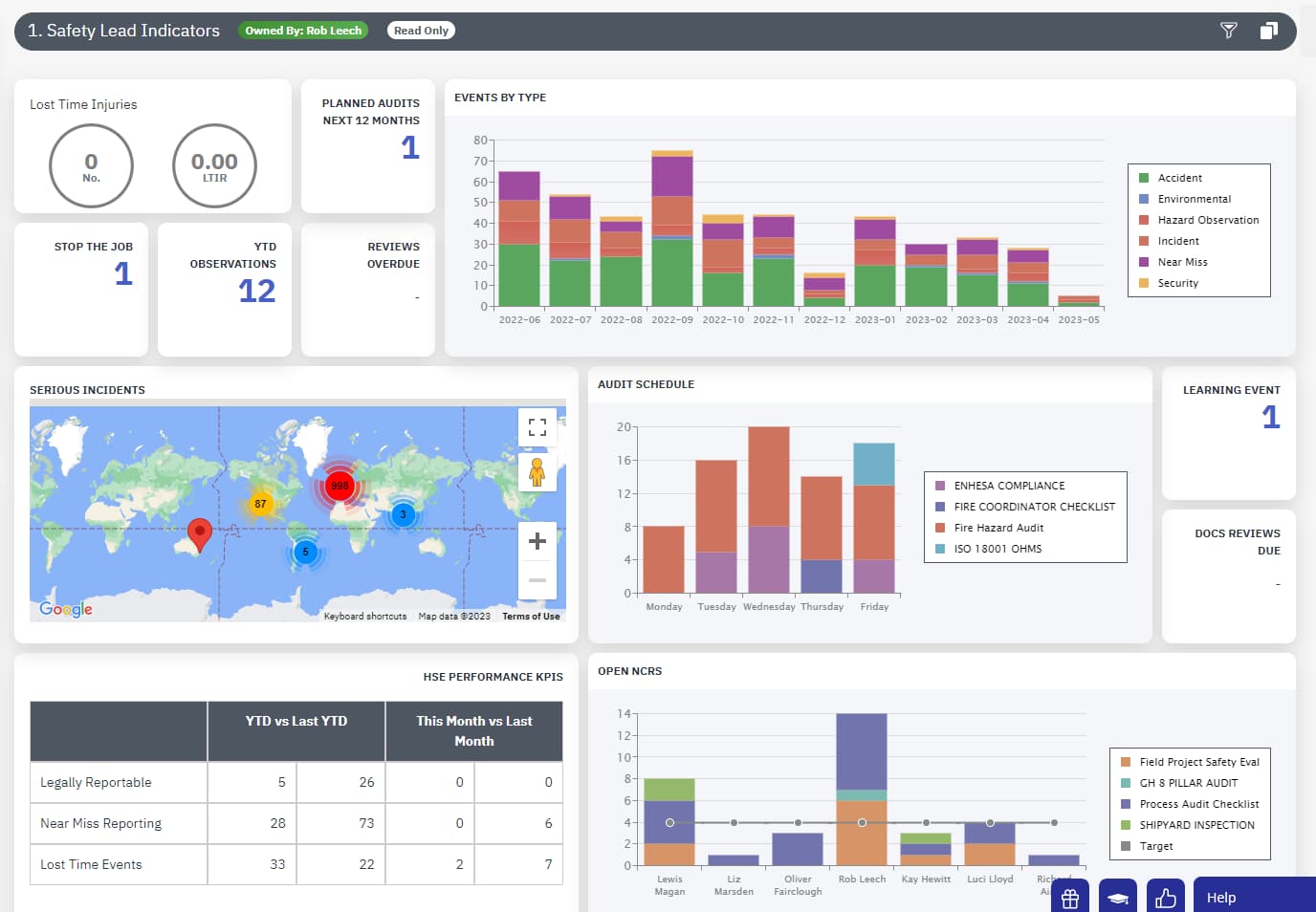
Use EcoOnline to Monitor Hazards and Overall Safety Performance
EcoOnline is a workplace safety solution that helps companies monitor safety performance and make their workplace safer. The EcoOnline Health & Safety Software makes it easy for companies to assess risk, prepare safety reports, and manage safety audits.
It’s a modular tool that includes root cause analysis software, and can be used to empower employees by giving them the tool to report hazards, build checklists, and even create and manage work permits.