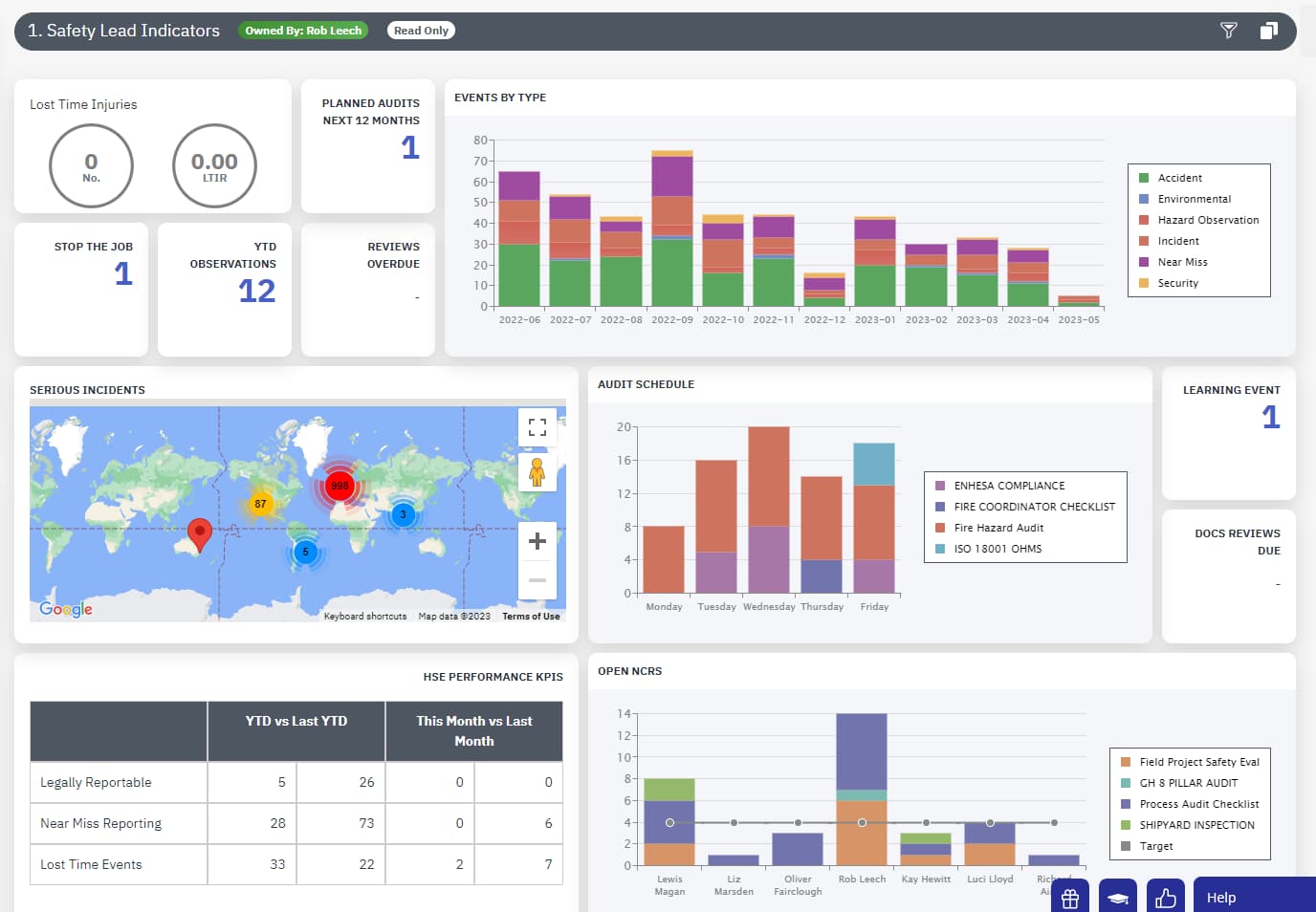
Lost Time Injury
What is Lost Time Injury?
Lost time injuries are a vital benchmark for any organization concerned with the health and safety of its employees.
These incidents have immediate consequences and long-term effects on both the injured employees and employers.
By fully understanding what lost time injury is, its implications, and prevention measures, Environment, Health, and Safety (EHS) teams can better implement strategies for mitigating risks and promoting a safer working environment.
Lost time injuries can have serious negative consequences for your business.
Lost Time Injury (LTI) refers to any work-related injury or illness that results in an employee being unable to perform their regular duties and requires them to take time off from work.
The time lost can vary from a day, weeks, or even months depending on the severity of the injury.
LTI is commonly used as a key performance indicator (KPI) to measure workplace safety performance and calculate injury frequency rates – the higher the frequency rate, the higher the risk of accidents within an organization.
The Impact of Lost Time Injuries on Business
The consequences of lost time injuries on businesses can be wide-ranging and severe. LTIs can hurt an organization in various ways, including:
- Financial costs associated with worker’s compensation and lost productivity
- Lowered employee morale and engagement
- Potential damage to the company’s reputation
Furthermore, LTIs can lead to compliance issues with regulatory bodies, which may result in fines, penalties or even shutdowns for non-compliance.
In some industries, LTIs can also impact a company’s ability to secure new contracts, as clients may prefer to partner with organizations that demonstrate a strong commitment to workplace safety.
How to Prevent and Mitigate LTIs
Given the significant consequences of LTI incidents, EHS teams should prioritize preventative measures to minimize the risk of workplace injuries.
Several strategies can help EHS teams effectively address LTIs, including the following:
Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
By identifying potential workplace hazards and assessing their associated risks, EHS teams can proactively address safety concerns before incidents occur.
A thorough risk assessment should consider both employees’ tasks and their working environment and be updated as changes in work processes or equipment occur.
The risks can be classified into three main categories – physical, organizational, and personal. Physical risks include unsafe working conditions and inadequately maintained equipment.
Organizational risks consist of factors like poor management, inadequate training or supervision, and absence of safety culture.
Personal risks involve employee-related factors such as lack of awareness, insufficient skill set, or non-adherence to safety protocols.
Implement Safety Training Programs
Ensuring that employees are educated on safe work practices and emergency response procedures can help prevent workplace injuries.
EHS teams should also track the completion of safety training sessions and ensure that employees are held accountable for their safety knowledge.
Develop and Enforce Safety Policies
Well-documented safety policies and procedures lay the foundation for a safe work environment.
EHS teams should ensure that safety policies are easily accessible to employees and that they are enforced consistently across the organization.
Encourage Employee Involvement
Engaging employees in safety initiatives can foster a strong safety culture and demonstrate that worker safety is a shared responsibility.
EHS teams may consider implementing safety committees, offering safety incentives, or instituting an employee safety suggestion program.
Monitor and Review Safety Performance
Regularly reviewing safety performance data can help EHS teams identify areas of improvement and track the effectiveness of their safety initiatives.
This may include monitoring Lost Time Injury Frequency Rates (LTIFR) and instituting corrective actions when performance falls below desired levels.
Implement a Strong Safety Culture
Promoting a strong safety culture across the organization is crucial in preventing lost time injuries.
This involves active engagement and commitment from all levels of the organization – from top management to frontline employees.
Elements of a strong safety culture include clear communication of safety goals and expectations, ongoing training and education, proactive hazard identification and mitigation, and celebrating safety successes.
By fostering a culture where employees feel empowered to report hazards and near misses, as well as actively participate in safety initiatives, it becomes easier for the EHS team to identify and address potential risks.
Use EcoOnline to Prevent and Mitigate Lost Time Injury
EcoOnline is one of the best platforms for companies that want to improve overall safety and reduce lost time injuries. Companies can use this workplace safety software to better understand common sources of workplace injuries and then take steps to mitigate or prevent them.