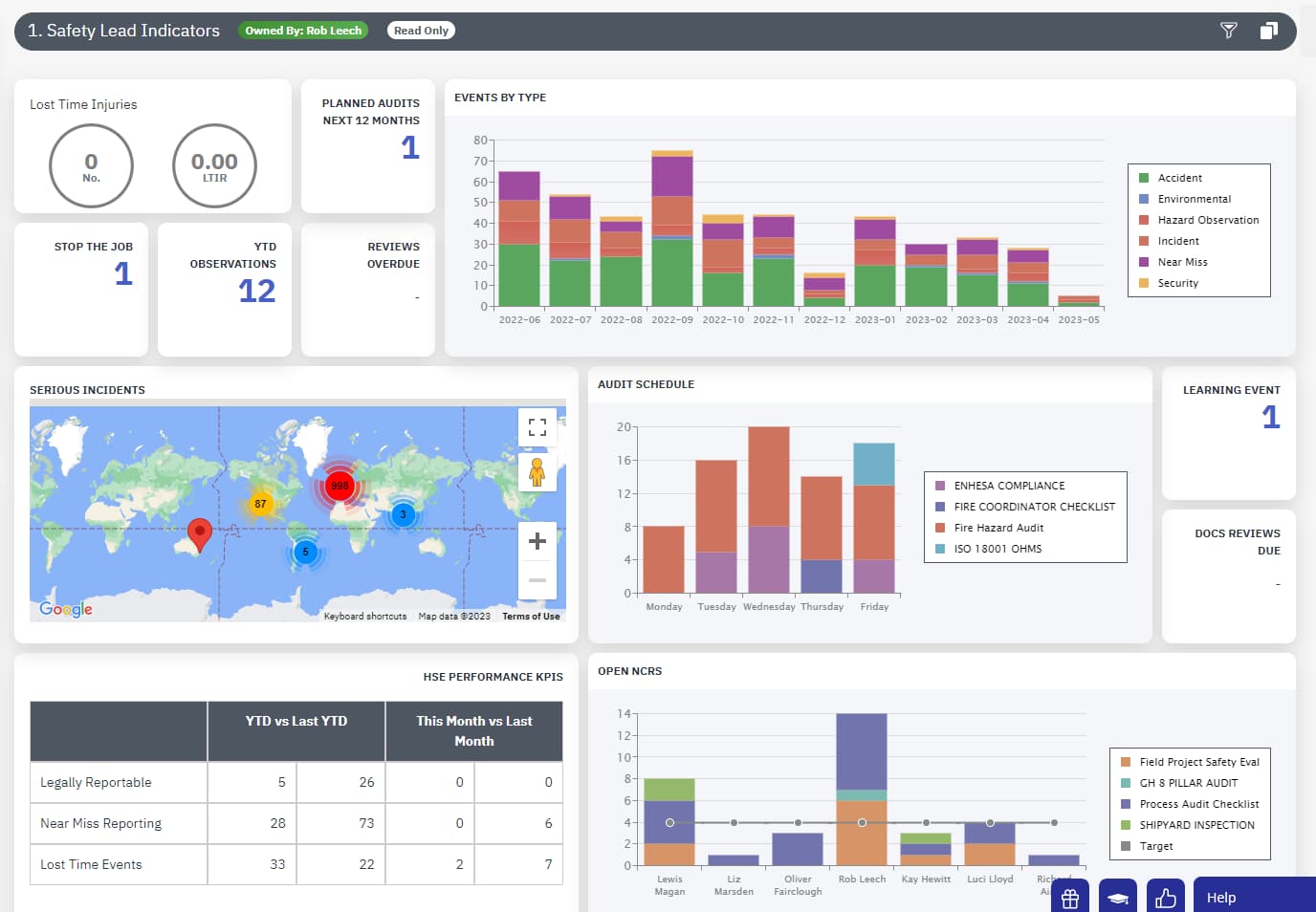
Occupational Exposure Limit
What are Occupational Exposure Limits?
Occupational Exposure Limits (OELs) are guidelines developed by regulatory bodies to promote worker health and safety and prevent the harmful effects of chemical exposure in the workplace.
OELs are legally enforceable limits on the amount or concentration of a particular chemical in the air that a worker can be exposed to over a specific period.
OEL refers to the level of exposure to hazardous substances in the air that a worker can be exposed to without experiencing any adverse health effects.
The main aim of setting OELs is to prevent overexposure to harmful substances, which can cause acute or chronic health effects.
Understanding OELs is essential for any organization that deals with hazardous materials or chemicals in order to ensure that their workers are not exposed to harmful levels of these substances.
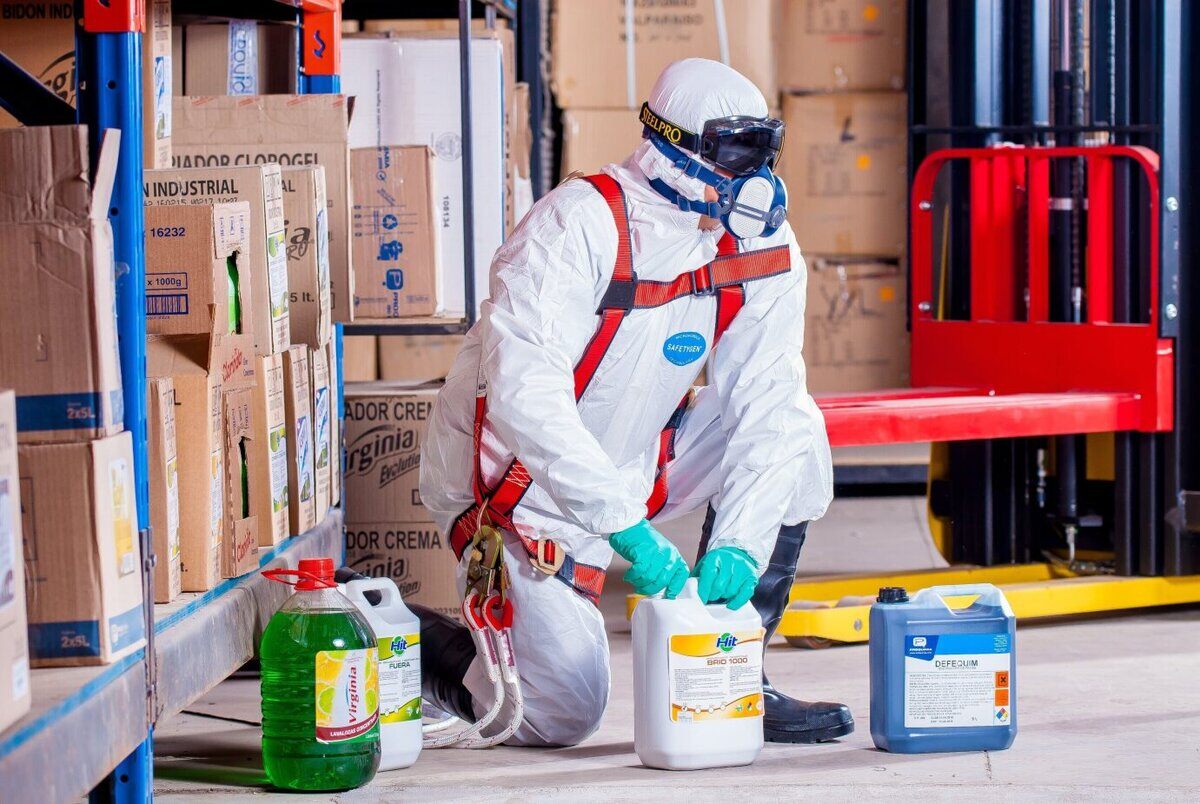

How Are OELs Determined?
OELs are typically established by regulatory agencies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States or the European Union’s European Agency for Safety and Health at Work (EU-OSHA).
These agencies identify and evaluate the health risks associated with chemicals based on scientific evidence and data.
This limit is usually expressed as a concentration measurement such as parts per million (ppm), milligrams per cubic meter (mg/m³), or micrograms per cubic meter (µg/m³).
The OEL is determined based on the toxicity of the substance, the duration and frequency of exposure, and the route of exposure.
They also set exposure limits that are designed to protect workers from the harmful effects of chemical exposure.
The Importance of Establishing OELs
Setting OELs is vital to protecting workers’ health and safety in the workplace. It helps employers to identify hazards and implement appropriate control measures to minimize or eliminate exposure.
Furthermore, it enables employees to identify dangerous situations and take necessary precautions to reduce their risk of exposure.
OELs are also essential in creating standards for hazardous substances and in enforcing regulations to protect the workers.
Without OELs, workers and their communities may be exposed to hazardous substances unknowingly, causing long-term health problems.
Factors to Consider When Establishing OELs
Several factors are taken into account when setting OELs, including the following:
- Individual susceptibility: Some workers may be more sensitive to certain chemicals and require lower exposure limits.
- The nature of the chemical: Some chemicals are more toxic than others, and therefore, require lower exposure limits.
- The exposure route: Depending on how a chemical enters the body, different exposure limits may need to be set. For example, chemicals that are inhaled into the lungs may require lower exposure limits compared to substances that are absorbed through the skin.
- The duration of exposure: Exposure limits are often set based on an average exposure time, typically an 8-hour day.
What are the Different Types of OELs
There are two types of OELs: time-weighted averages (TWAs) and short-term exposure limits (STELs). TWA is the average concentration of a chemical in the air over an 8-hour workday.
STELs, on the other hand, are short-term limits that are meant to protect workers from exposure to high concentrations of a chemical for short periods of time, typically 15 to 30 minutes.
Control Measures Against Overexposure
Employers have a legal obligation to protect their workers from exposure to hazardous substances.
These obligations may include providing personal protective equipment (PPE), adopting engineering controls such as ventilation systems, and implementing safe work practices such as job rotation.
Workers also have a responsibility to use PPE correctly, follow safe work practices, and report any health concerns. A combination of these control measures and effective OEL monitoring can help maintain a safe and healthy work environment.
Consequences of Not Adhering to OELs
Organizations that fail to adhere to OELs face serious consequences, including:
- Reputational damage: Companies that fail to protect their workers from harmful exposure to chemicals can damage their reputation, leading to a loss of business and reduced profitability.
- Fines and penalties: Failure to comply with OELs can result in significant fines and penalties imposed by regulatory agencies.
- Lawsuits: Workers who are exposed to high levels of chemicals or substances that exceed OELs may suffer from health problems and can file lawsuits against their employers.
How to Prevent Injuries from Manual Handling
Employers have a responsibility to reduce the risks associated with manual handling by implementing preventive measures. The most effective approach is to eliminate or reduce manual handling tasks that pose a high risk of injury. If it is not possible, employers can implement the following measures to minimize injury risks:
- Train workers in proper lifting techniques and body posture
- Provide specialized equipment such as lifting aids or trolleys
- Implement job rotation to ensure that workers do not spend long periods performing manual handling tasks
- Conduct regular assessments of manual handling tasks to reduce the risk of injury
Use EcoOnline to Manage Occupational Exposure Limits
Occupational Exposure Limits are a critical element in protecting workers from exposure to hazardous chemicals in the workplace.
By establishing acceptable exposure limits, regulatory agencies ensure that organizations take the necessary steps to ensure worker safety.
EcoOnline’s Health and Safety Software allows companies to manage occupational exposure limits carefully, allowing companies to monitor safety results and glean data-driven insights about exposure limits and their effectiveness.