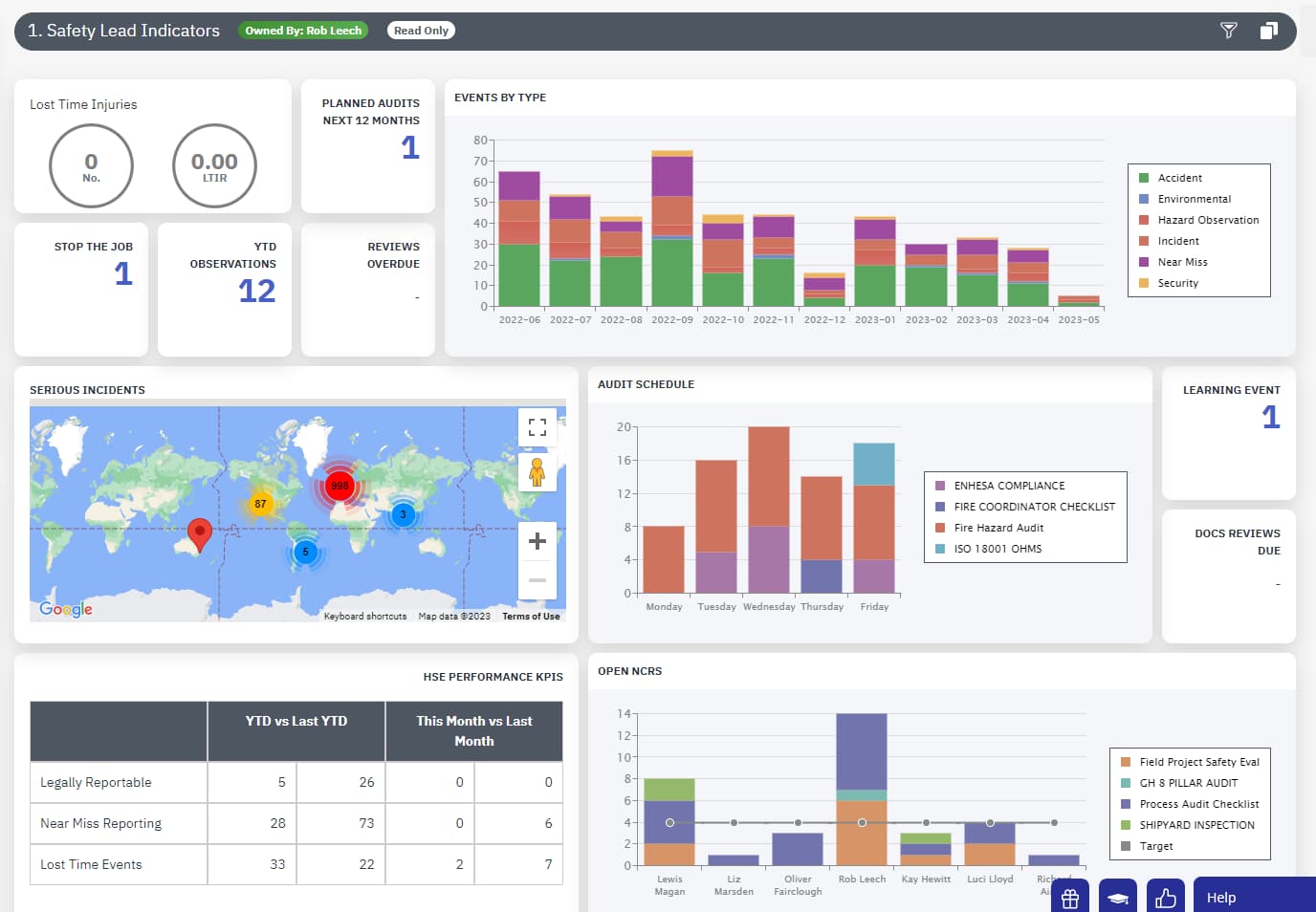
Occupational Illness Meaning & Definition
What is an Occupational Illness?
An occupational illness is defined as a chronic illness or disease that is caused primarily due to exposure to a workplace hazard. Typically, occupational illnesses generally manifest due to prolonged exposure to such hazards, including harmful chemicals or materials.
Any illness caused due to exposure to a workplace hazard is an occupational illness. It is necessary for employers to ensure that they provide a safer work environment to employees and to reduce the spread of occupational illnesses or diseases.
However, it’s generally a bit difficult to prevent occupational illnesses, as illnesses usually develop over a longer period of time. Thus, establishing a relation between cause and effect is generally not easy. By the time the symptoms appear, some illnesses usually advance to a stage where they require extensive treatment.

Is incident reporting the key to culture change? Get this 17-page guide discussing how reporting incidents, close calls and observations can help transform your safety culture.
Why Are Occupational Illnesses Important?
For a business, it’s incredibly important to take steps to mitigate occupational illnesses and diseases. They pose a serious threat to business continuity and could result in a litany of lawsuits that could affect the company’s going concern.
More importantly, occupational illnesses result in lost work hours, with employees losing productivity and not being able to work. The business then bears the losses, as employees often require compensation while they rest.
How to Define an Occupational Illness
Occupational illnesses can be defined through a specific criteria, which varies depending upon local legislation. However, according to a research paper published in Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine #58, there are nine points that can be used to identify occupational illnesses:
- Cause and effect (the strength of the relationship between the two)
- Consistency between the results
- Is there a direct, one-to-one relationship between the cause and effect?
- Did exposure occur before the effects materialized?
- Overall biological trend (response to dosage or identified health effects)
- Are the cause and effect plausible?
- Is the association between the cause and effect coherent?
- Any experimental or untested evidence
- Analogous evidence (similar cases)
If these criteria are met, then an illness can be described as an occupational illness.
The Most Common Occupational Illnesses
There are several common occupational illnesses that you should know about. Many of these are caused due to factors at work and can be mitigated if appropriate safety measures are taken.
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL)
Noise-induced hearing loss occurs due to excessive exposure to ambient noise, which eventually causes irreversible damage to a person’s eardrums. The damage caused is permanent, with workers being eligible to file a compensation claim against their employer.
The Health and Safety Executive in the UK estimated that more than 2 million people are exposed to dangerously high noise levels at work. 75% of all health insurance claims (work-related) are for NIHL.
Occupational Dermatitis
Dermatitis is a type of skin infection that results in inflammation. It’s usually caused due to the presence of skin irritants or allergens in the work environment.
The symptoms usually manifest slowly and are often progressive in nature. Dermatitis causes the upper layer of the skin to break, resulting in rashes that tend to sting.
It also results in blisters and causes itchiness. In most cases occupational dermatitis appears in the hands and forearms, and is mostly caused when employees touch substances or materials that they’re allergic to.
Respiratory Diseases
Respiratory diseases include all diseases and illnesses that affect a person’s respiratory system. These generally include diseases such as asthma, COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases), bronchitis, emphysema, lung cancer, or pleural effusion.
Respiratory illnesses can be caused due to the inhalation of harmful substances or vapours in the workplace. There are several industries in which respiratory illnesses are more prevalent, including foam or plastic manufacturing, or the auto parts industry.
Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs)
Musculoskeletal disorders are perhaps the easiest to prevent. These include any disorders or injuries that are caused due to poor ergonomics in the workplace or a bad posture.
Repetitive strain injuries, like carpal tunnel syndrome or tendonitis, are also included in this category. These are essentially injuries that are caused due to performing repetitive movements.
Stress, Anxiety, and Other Mental Health Disorders
Mental health disorders are becoming increasingly common in modern workplaces. Stress-induced anxiety, for instance, is a common example.
There are many cases of workers suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD. This is caused due to high-pressure work environments, or due to the occurrence of a traumatic event in the workplace.
Another mental disorder that many employees suffer from is depression. Depression is caused due to low self-esteem, a poor work environment, or lack of support from colleagues.
Manage Occupational Illnesses and Reduce Stress with EcoOnline’s Health & Safety Software
EcoOnline’s Health & Safety Software is designed to improve reporting in the workplace and generally enhance worker safety. From building checklists to conducting inspections and identifying hazards that could result in occupational illnesses, it is an all-in-one platform with custom modules that can be tailored to a business’ specific requirements.